Jaw Fracture
The potential for a jaw fracture is more common than is readily apparent. Various types of scenarios can result in a lower jawbone (mandibular) fracture including, a motor vehicle crash, sports injuries, assault, or even a simple fall. Fracture of the lower jawbone can be extremely painful and potentially debilitating if not properly addressed.
Jaw Anatomy
What are the different regions of the lower jawbone?
The lower jawbone is a single bone that is divided into six main regions. Depending on the method of injury, any of these regions can be affected. The location of a fracture then dictates the type of presentation, symptoms and ultimately the treatment.
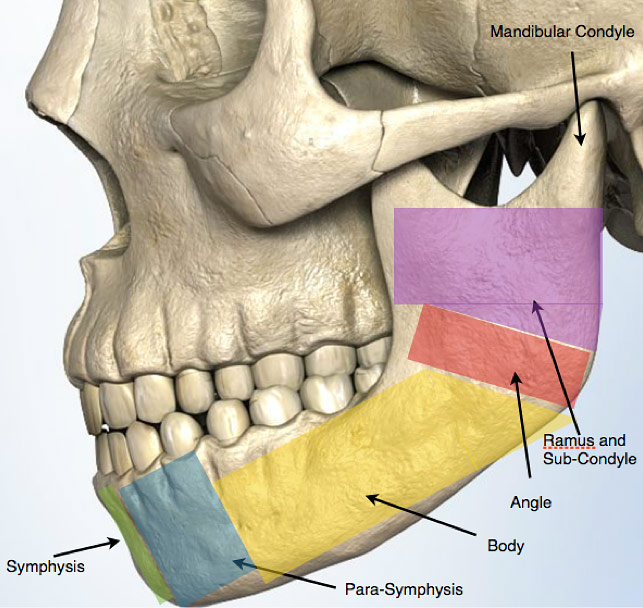
Figure 1: Schematic of the mandible (lower jawbone) and its 6 regions.
Diagnosis
How do I know if my jaw is broken?
Trauma to the lower jaw can result in single or multiple fractures at any of the jaw’s different regions. Symptoms are usually dependent on the location of the fracture. However, because the jawbone is mobile, one of the first symptoms can be severe pain over the site of the fracture with opening and closing of the mouth. The pain can in fact be severe enough that the mouth can only be opened a small amount, a condition referred to as “trismus”. Chewing will be extremely difficult and painful. At times pain may not be present or severe but the patient may experience a crunching or movement of the jaw with chewing. Oftentimes a condition known as, “malocclusion” will be evident where the upper and lower teeth do not fit or make proper contact with each other. In rare circumstances, progressive swelling and bleeding from the floor of the mouth may occur, requiring emergency medical attention.
In all cases of suspected jaw fracture, prompt evaluation is strongly advised.
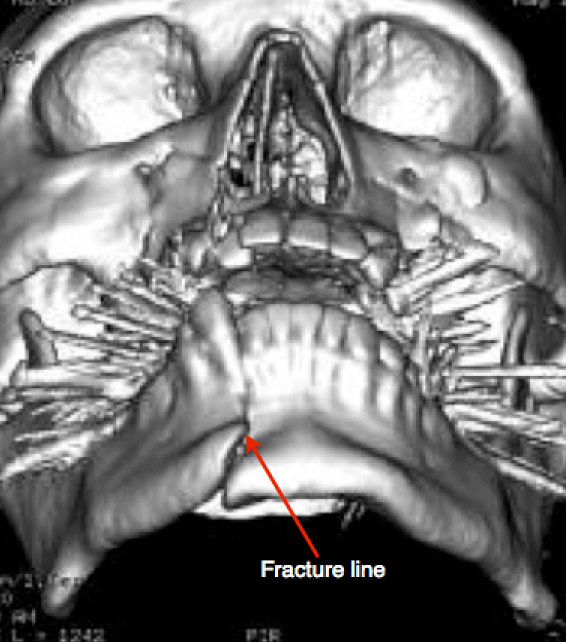
Figure 2: 3D-CT reconstruction of the skull demonstrating a fracture of the mandibular para-symphysis and a shift in teeth position.
I think I broke my jaw. Now what?
If you suspect that you have a jaw fracture prompt evaluation and treatment are highly advisable. You can confirm the presence of a jaw fracture with a CT scan and be evaluated for other potential injuries at a local emergency room. Once a diagnosis of mandibular fracture has been confirmed, reconstructive surgery form a qualified facial trauma specialist is recommended to ensure that your fracture is appropriately repaired.
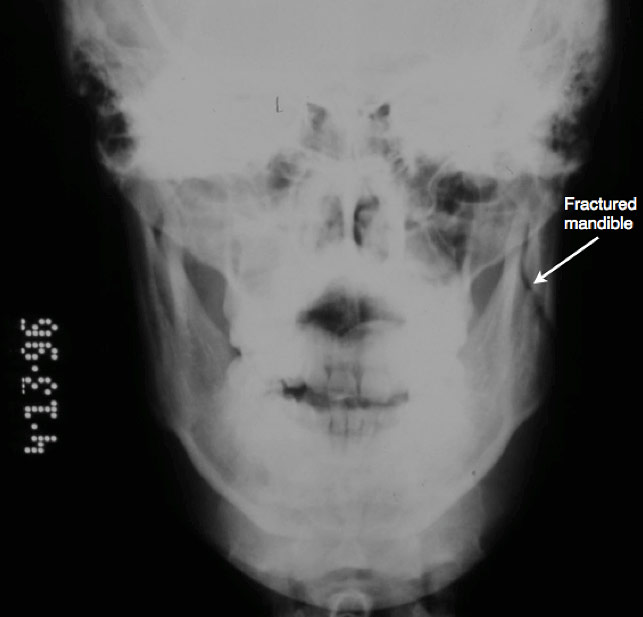
Figure 3: A plain X-ray of the face showing a fracture of mandibular ramus with limited shift in teeth position. This patient experienced difficulty opening and closing the mouth.
Treatment
How is my fracture repaired?
Mandibular fracture treatment depends on the site and the extent of the fracture. In most cases a fracture can be repaired using small incisions that are hidden in the gum lines of the mouth. Special thin plates and materials are then placed directly onto the bone fragments to stabilize the fracture. In some instances temporary braces may be placed to preserve your normal bite pattern during healing.
Although commonly performed by many surgeons, wiring of the jaw should be avoided as a treatment option for mandibular fractures. Jaw wiring commonly leads to slower recovery, jaw joint (temporomandibular joint or TMJ) problems, difficulty speaking, and a severely restricted diet. In addition jaw wiring creates a potentially life-threatening situation because it obstructs the normal passageway of a choking or vomiting individual.

